
Ultra-wideband (UWB) isn’t just a feature tucked inside your phone or car key—it’s a foundational technology reshaping how people, devices, and systems interact with the world around them. From smart homes to factories and public transit systems, UWB is powering a new era of location-aware, secure, and automated experiences. Now, a global economic study commissioned by the FiRa® Consortium and conducted by Telecom Advisory Services reveals the full extent of UWB’s economic and societal value, and the findings are transformative.
The Big Picture: UWB’s $36.8 Billion Opportunity by 2030
According to the study, UWB will generate $36.8 billion in global socio-economic value by 2030, a leap from $10.5 billion in 2024. This surge is driven by rapid growth in:
- UWB-enabled smartphones and wearables
- Automotive applications like digital car keys and in-cabin sensing
- Industrial automation, including real-time location systems (RTLS)
- Retail, healthcare, public transportation, and smart infrastructure
More than 1.5 billion UWB-enabled devices were already shipped by the end of 2023, and that figure is expected to rise to 1.4 billion devices annually by 2029.
A Clear Growth Curve
UWB’s global value is growing rapidly, driven by expanding adoption across smartphones, vehicles, infrastructure, and industrial equipment. With its ability to enable secure, ultra-precise location and access functionality, UWB is being built into the digital backbone of modern economies. The study quantifies this momentum, providing a year-over-year snapshot of accelerating value creation.
Key Projections:
- Global Value Growth: $10.5 billion in 2024 to $36.8 billion in 2030
- Device Growth: From 1.5 billion cumulative shipments by 2023 to 1.4 billion devices shipped annually by 2029
- Primary Adoption Drivers: Integration into mobile devices, automotive ecosystems, smart infrastructure, and industry
This growth curve reflects both an increasing range of UWB use cases and expanding device ecosystems. UWB is not only spreading across sectors, it’s scaling within them, creating more value with every new application.
How UWB Creates Economic Value
Unlike traditional wireless technology, where value is tied to network infrastructure or spectrum licensing, UWB creates value through precision-driven outcomes: operational efficiency, safety, time savings, and user-centric experiences. The study quantifies UWB’s economic contributions across three pillars that together define UWB’s financial impact across both public and private sectors:
- GDP Contribution
Revenues from UWB-enabled products and services directly increase national GDP, especially in tech-forward economies. 2022: $1.8B → 2030: $6.5B - Producer Surplus
Organizations using UWB benefit from lower costs, better automation, and reduced waste—especially in manufacturing, retail, logistics, and healthcare. 2022: $1.9B → 2030: $15.2B - Consumer Surplus
UWB applications simplify daily tasks, save time, and increase security. Over time, these benefits accumulate into tangible economic value for individuals and households. 2022: $3.1B → 2030: $14.9B
Use Case Growth: Where UWB Is Taking Off
The economic impact of UWB varies depending on how and where it’s deployed. The study segments growth across key verticals, offering a granular view of where the technology delivers the most value today, and where future opportunities lie. Each sector is defined by unique dynamics, from household convenience to industrial logistics and transit automation.
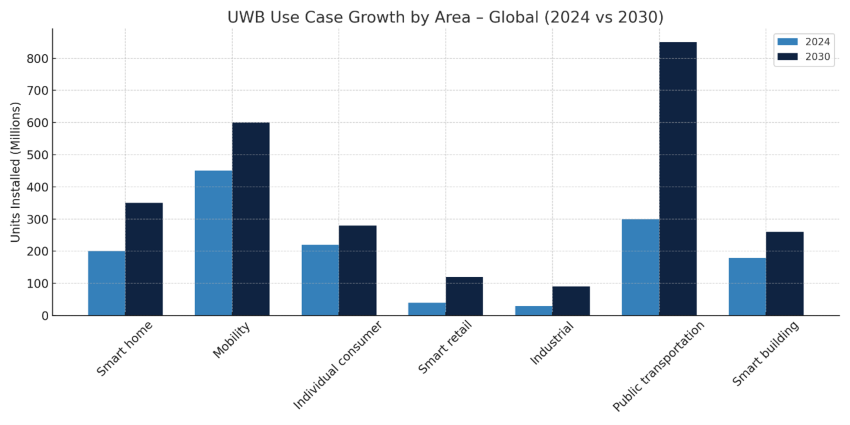
Across these verticals, mobility and retail applications show the highest growth rates, while smart home and industrial solutions represent the largest overall volume increases. These numbers confirm what many in the field already suspect: UWB’s early footholds are fast becoming foundational pillars.
Country-Level Insights: UWB’s Growing Global Footprint
While UWB’s value creation is global, the distribution of that value is shaped by national policies, market maturity, industrial focus, and ecosystem readiness. The study offers detailed, country-level forecasts that highlight where UWB is having the biggest economic impact—and why.
Top 2030 Country Contributions:
- United States: $9.4B
Leading in mobility and smart retail; strong public-private investment. - China: $8.1B
Smart city and industrial IoT deployment at scale. - Germany & Japan: $6.7B and $5.6B
Innovation in automotive, healthcare, and smart manufacturing. - Brazil & Mexico: $3.6B and $2.0B
Rapid expansion in contactless retail, transit access, and automation. - Nigeria & South Africa: $1.3B+ combined
High efficiency gains per dollar invested in public and healthcare sectors.
These figures show that UWB is not just a “developed market” story. In emerging economies, the return on investment is often even higher due to leap-frogging potential and the absence of legacy constraints. Governments and businesses in these regions have much to gain from proactive adoption.
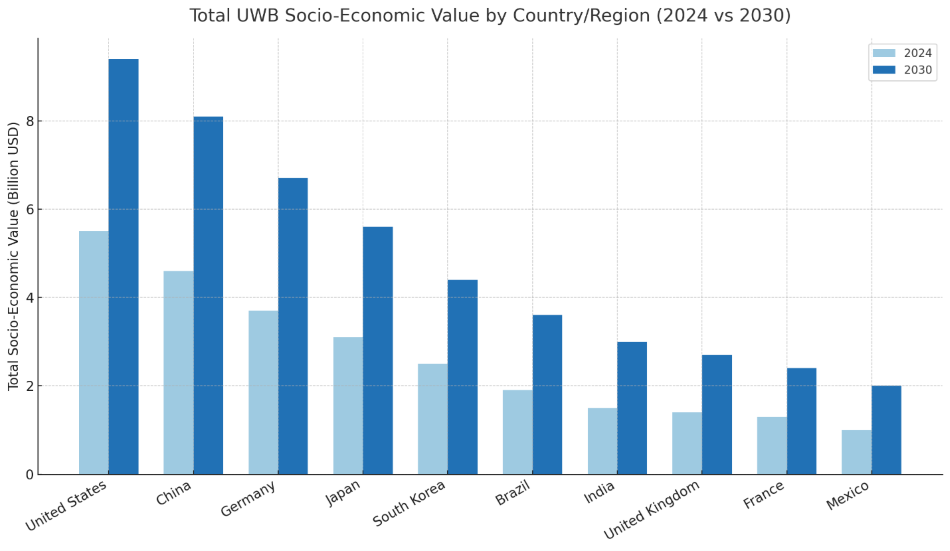
Even emerging markets with lower per-device adoption rates—such as Nigeria, South Africa, and Indonesia—show disproportionately high productivity gains per dollar invested, indicating enormous potential for leapfrogging legacy systems.
Societal Value: Beyond Economics
Not all of UWB’s value can be measured in dollars, and that’s part of what makes it so transformative. The technology delivers critical improvements in public safety, accessibility, healthcare, and quality of life. These benefits may not show up on a balance sheet, but they’re deeply felt across communities and organizations.
Key Social Benefits:
- Public Safety: Firefighter tracking, child presence detection, secure access to hazardous zones.
- Healthcare: Patient monitoring, touchless records access, proximity alerts for vulnerable populations.
- Accessibility: Context-aware automation for the elderly or people with disabilities.
- Environmental Impact: Energy savings via presence-based smart home and building systems.
These contributions underscore UWB’s role as more than a commercial enabler—it’s a technology for public good. In a world where time, safety, and trust matter more than ever, UWB supports systems that are not only more efficient but also more human-centric.
Future Growth: Where the Numbers Accelerate
Two key trends will push UWB's value curve even higher by 2030:
- Massive Device Ecosystems:
UWB is being embedded in phones, cars, wearables, home systems, industrial tags, and transit infrastructure. Cross-sector adoption multiplies value exponentially. - Converging Standards and Interoperability:
Led by organizations like the FiRa Consortium, global interoperability frameworks will allow devices from different vendors and sectors to communicate securely, driving even broader uptake.
UWB: Built for What Comes Next
The data is clear: UWB is not just a wireless technology; it’s a high-impact platform that is quietly revolutionizing connectivity. With a projected $36.8 billion global economic contribution by 2030, widespread adoption, and critical social applications, UWB is transitioning from potential to essential.
Now is the time for stakeholders—governments, enterprises, developers, and standards bodies—to invest in infrastructure, education, and interoperability. The path forward isn’t just about faster connections; it’s about smarter, safer, and more connected systems across every sector.